Unraveling the "Google Patient" Phenomenon: Challenges and Navigating Solutions for Healthcare Professionals
In today’s world, where information is just a click away, a new trend has become increasingly noticeable in healthcare: the "Google Patient."
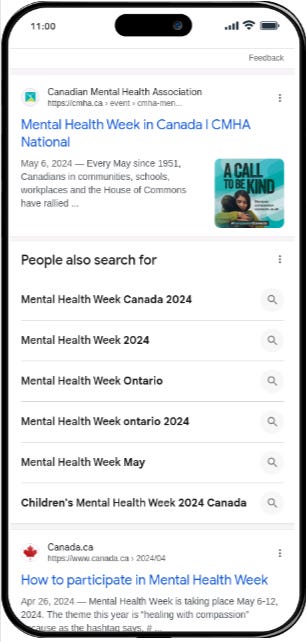
May is Mental Health Awareness Month. This occasion has allowed me to once again validate the support that can be obtained from search engines on the subject of mental health. It must be admitted that Google has done a very good job when, for example, one searches for information on Mental Health Week, Google redirects them to government websites and credible sources.
However, as mentioned on numerous occasion, not all the people concerned by these issues are aware that, when they are experiencing a mental health disorder, the answers already exist on appropriate websites. The issue is getting access to these relavant websites.
For example, this year the theme of Mental Health Week was compassion https://cmha.ca/mental-health-week/
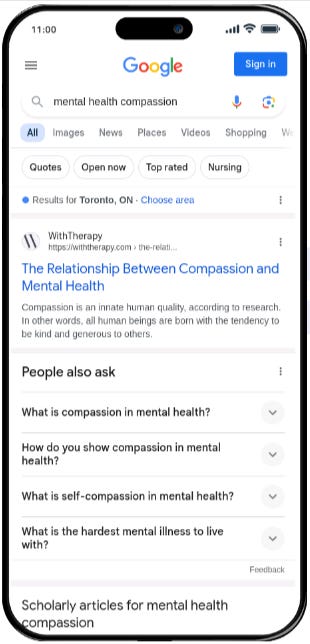
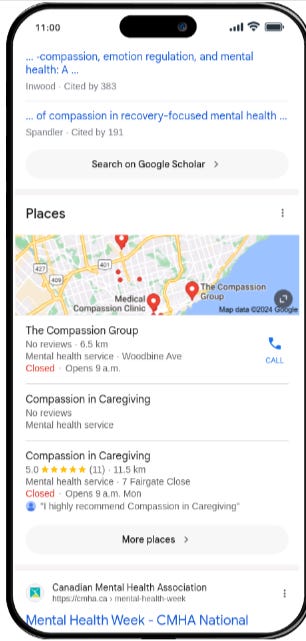
If you type this query on google “mental health compassion” you can no longer find the authoritative and credible sites to help the population on top of google results pages
You will have to scroll down to find a few pages of the CMHA and then nothing more. This highlights the urgency for health professionals to implement good SEO practices.
Solving this situation is becoming urgent. Mental health remains a top concern for Canadians, as evidenced by continued high search volumes for related topics on search engines. But the quality of search results is lacking.
Key Points:
Mental Health Awareness Month is an opportunity to highlight the importance of mental health and the resources available to support those in need.
Search engines can be a valuable tool for finding information about mental health, but the quality of results can vary.
It is important for mental health professionals to use good SEO practices to ensure that their websites are visible to those who need them.
Canadians are increasingly searching for information about mental health online, but there is a need for more high-quality resources.
The google patient phenomenon
80% of internet users have searched for a health-related topic online, according to the Pew Research Center.
Cyberchondria" affects about one in five hospital patients, escalating concerns about common symptoms based on online searches, notes the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
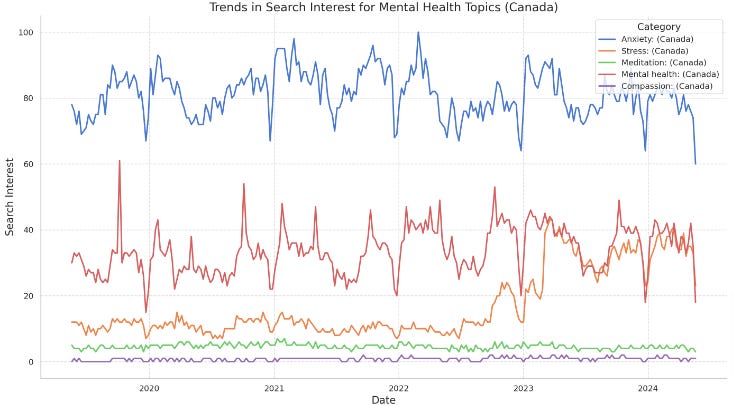
When looking at search interest for the last 5 years, mental health searches remains trendy.
High and Consistent Interest in Anxiety:
Anxiety consistently shows the highest search interest among the mental health topics throughout the period, indicating a significant and ongoing concern among Canadians.
Moderate Interest in Mental Health and Stress:
Mental health and stress have moderate and relatively stable interest levels, suggesting steady awareness and concern about these issues without significant spikes or declines.
Low but Stable Interest in Meditation and Compassion:
Meditation and compassion have the lowest search interest, with little variation over time. This may indicate a lower public focus or awareness on these topics compared to anxiety and mental health.
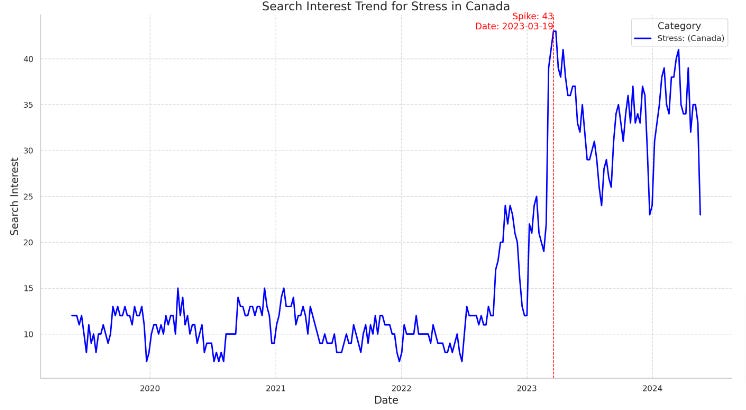
A detailed analysis of the “stress'“ searches in canada is revealing of an increasing public discourse about stress during this period since march 2023.
The “Google patient phenomenon” refers to the trend of individuals searching for medical information on the internet, often before consulting with a healthcare professional. This behavior has become so common that it has been given the name Cyberchondria, which is the condition of health anxiety induced by self-diagnosis on the internet.
Risks and Implications for Healthcare Professionals
Misdiagnosis and Increased Anxiety
Patients often come to consultations with specific ideas about what ails them, ideas rooted in online searches that may not be accurate. This misinformation can lead to unnecessary anxiety and a mismatch between their expectations and the doctor’s diagnosis.
Erosion of Trust
When a patient’s findings from the internet clash with a professional’s advice, it can undermine trust. This skepticism may cause patients to question their doctor’s expertise or seek second opinions, complicating their treatment.
Inefficient Consultations
Armed with extensive but not always accurate information, patients can prolong consultations as doctors spend time debunking myths and correcting misinterpretations. This not only strains resources but also affects the efficiency of medical practice. As we delve deeper into these challenges, understanding the influence of major search engines in shaping digital health information becomes crucial.
Strategies for Healthcare Professionals
1. Embrace the Informed Patient
Rather than viewing patient research as a hurdle, healthcare providers should see it as an opportunity to engage in richer, more informed dialogues. By directing patients to trustworthy sources and helping them interpret complex medical information, professionals can enhance patient understanding and collaborative decision-making.
2. Develop Digital Resources
Healthcare providers can contribute by creating or endorsing online content that adheres to the highest standards of accuracy. Establishing reliable digital resources helps ensure patients access dependable information which supports their health journey.
3. Train in Digital Competency
It’s also beneficial for healthcare professionals to boost their digital skills. Understanding how to interact effectively with tech-savvy patients and navigating online medical information are crucial skills in today’s digital age.
Overall, while Google provides a valuable resource for patient education and engagement, it also poses challenges that need to be managed through better patient-physician communication and validated online resources. The "Google Patient" is a reality of modern healthcare that is here to stay. Adapting to this shift by enhancing digital interactions and guiding patients toward accurate information not only improves the quality of care but also streamlines the healthcare delivery process.
While looking up symptoms online can be quick and easy, it’s important to note that self-diagnosing via the internet can often be inaccurate. Studies have shown that online symptom-checking websites and apps list the correct diagnosis first only about 36%of the time.
Therefore, while these tools can be helpful, they should be used cautiously and not replace professional medical advice. Even Google recognize the danger of misinformation online. They introduced the "Google Medic Update" in August 2018. This significant algorithm adjustment aimed at enhancing the quality of information, especially for health and medical sites, prioritizing authority, expertise, and trustworthiness.
The initiative underscores the need for accurate, expert-verified medical information, which is essential for reducing misinformation and improving the foundation of healthcare consultations.
Of course we all know that, if you’re experiencing health concerns, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider who can offer a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis. But we should recognize that people are intensively turning to search engines and chatbots to find answers.
Sources
Recent Insights Into Cyberchondria | Current Psychiatry Reports - Springer. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11920-020-01179-8
Self-esteem and cyberchondria: The mediation effects of health anxiety .... https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12144-019-00216-x
Judging Online Health Misinformation: Effects of Cyberchondria and Age .... https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-34866-2_22
Recent Insights Into Cyberchondria - Springer. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11920-020-01179-8.pdf.